A Singles Chain is created by following a candidate which has only 2 occurrences in an area and creating a chain of cells with alternate colors (blue & pink). Looking at the chain allows us to see if there are potential solutions based on the cells in the chain.
If the chain contains 2 cells of the same color in the same area, it means that we have a conflict, therefore the solution cells are the ones which are colored with the opposite color.
If there is a cell which is not on the chain but also contains the candidate and it can see two different colored cells from the chain. Then we can elliminate the candidate from this cell.
If two cell of the same color are part of the same area, it means that that value cannot be the solution, as both cells cannot be off since one of them must be the solution.
If an off-chain cell's peers include 2 on-chain cells with different colors, then the off-chain cell cannot hold that candidate, since one of the on-chain cells will have to be the solution.
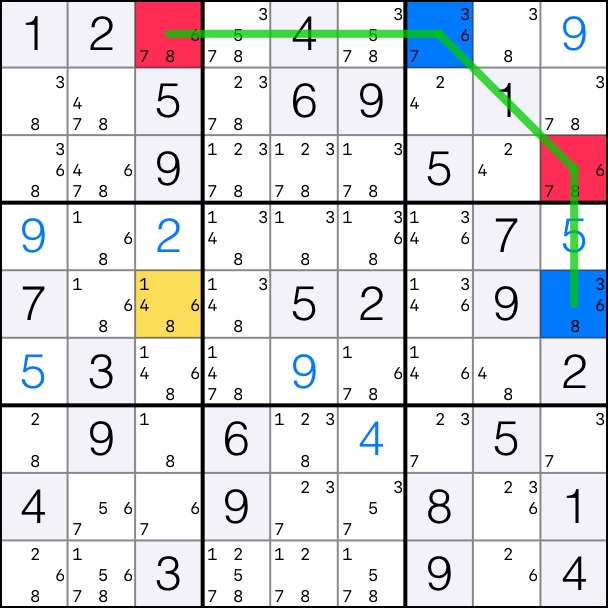
6-Singles Chain: Off-chain cell [5,3] can see both cell [1,3] and [5,9] which are on the chain and of different colors.
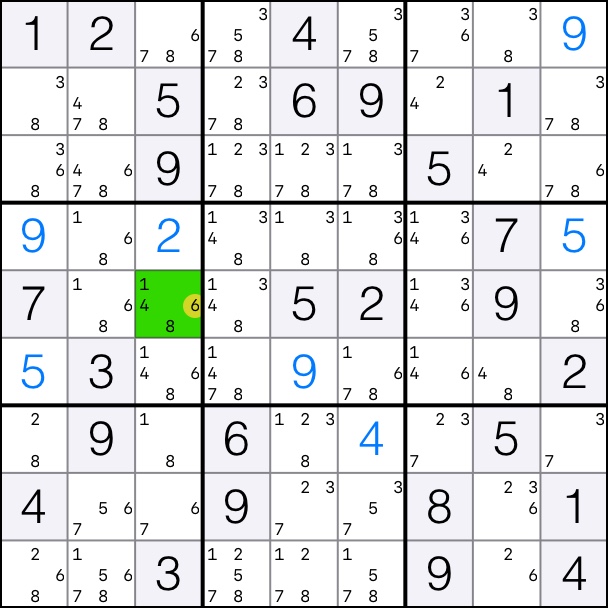
That means that candidates 6 can be removed from cell [5,3].
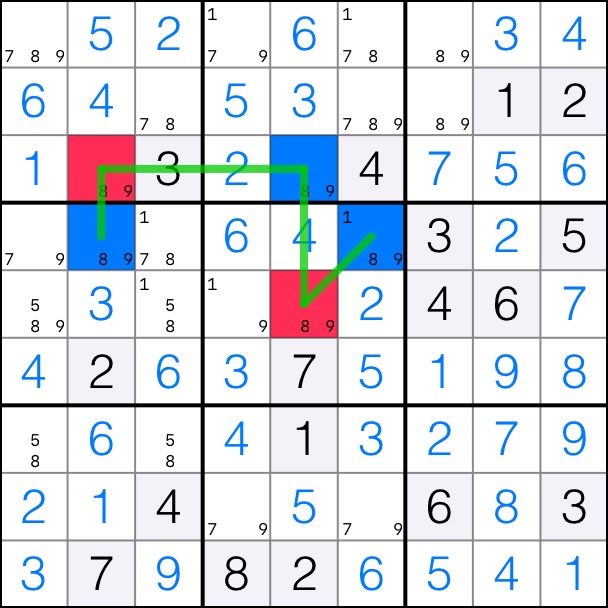
8-Singles Chain: Cells [4,2] and [4,6] are both blue.
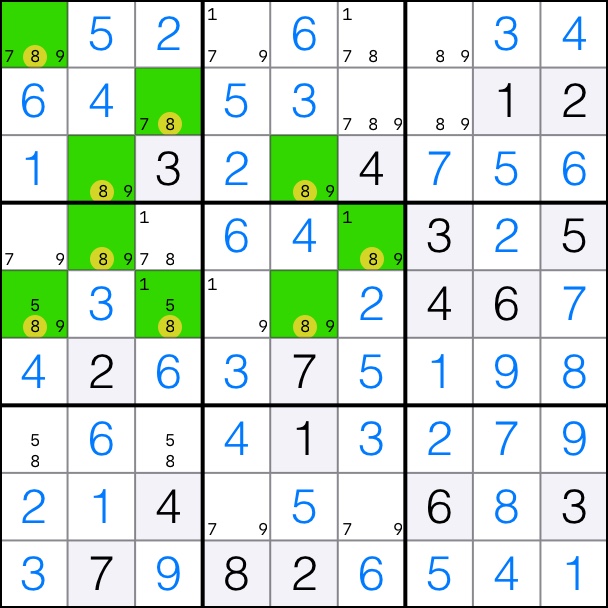
That means that the pink cells are the solutions in the chain. Cells [3,2] and [5,5] take on the value of 8.
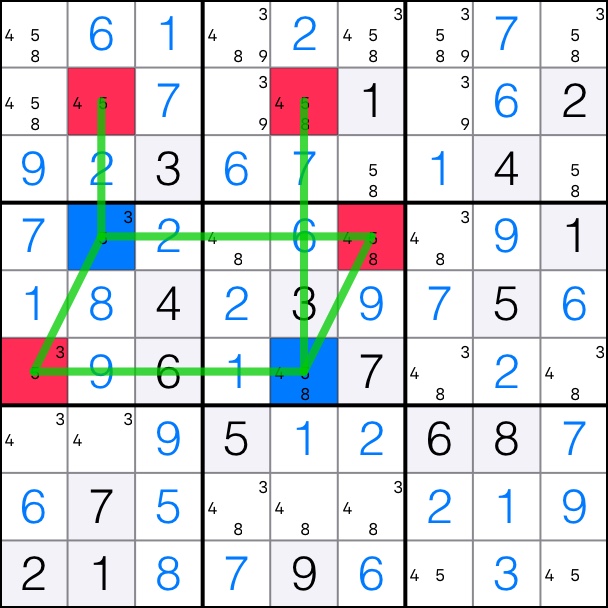
5-Singles Chain: Cells [2,2] and [2,4] are both pink.
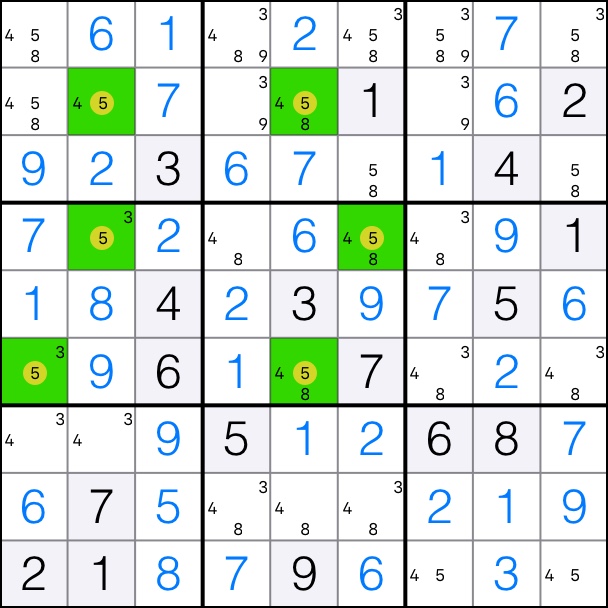
That means that the blue cells are the solutions in the chain. Cells [4,2] and [6,5] take on the value of 5.
This algorithm is currently not easy to do without paper and pencil. You can take a picture of the puzzle and print it, then follow the instructions below.
If you tap on the following links on an iOS device which has the Sudoku Tutor app installed, it will launch the app and open the practice puzzle. Tap hint once the puzzle is open to see the strategy in action.
Sample Puzzle 1 Sample Puzzle 2 Sample Puzzle 3Back to Sudoku Solvers or continue to next algorithm XY-Chain